Using Incremental Learning Job in Helmet Detection Scenario¶
This document introduces how to use incremental learning job in helmet detection scenario. Using the incremental learning job, our application can automatically retrains, evaluates, and updates models based on the data generated at the edge.
Helmet Detection Experiment¶
Install Sedna¶
Follow the Sedna installation document to install Sedna.
Prepare Model¶
In this example, we need to prepare base model and deploy model in advance. download models, including base model and deploy model.
cd /
wget https://kubeedge.obs.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com/examples/helmet-detection/models.tar.gz
tar -zxvf models.tar.gz
Prepare for Inference Worker¶
In this example, we simulate a inference worker for helmet detection, the worker will upload hard examples to HE_SAVED_URL, while
it inferences data from local video. We need to make following preparations:
make sure following localdirs exist
mkdir -p /incremental_learning/video/ mkdir -p /incremental_learning/he/ mkdir -p /data/helmet_detection mkdir /output
download video, unzip video.tar.gz, and put it into
/incremental_learning/video/
cd /incremental_learning/video/
wget https://kubeedge.obs.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com/examples/helmet-detection/video.tar.gz
tar -zxvf video.tar.gz
Prepare Image¶
This example uses the image:
kubeedge/sedna-example-incremental-learning-helmet-detection:v0.4.0
This image is generated by the script build_images.sh, used for creating training, eval and inference worker.
Create Incremental Job¶
In this example, $WORKER_NODE is a custom node, you can fill it which you actually run.
WORKER_NODE="edge-node"
Create Dataset
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: sedna.io/v1alpha1
kind: Dataset
metadata:
name: incremental-dataset
spec:
url: "/data/helmet_detection/train_data/train_data.txt"
format: "txt"
nodeName: $WORKER_NODE
EOF
Create Initial Model to simulate the initial model in incremental learning scenario.
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: sedna.io/v1alpha1
kind: Model
metadata:
name: initial-model
spec:
url : "/models/base_model"
format: "ckpt"
EOF
Create Deploy Model
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: sedna.io/v1alpha1
kind: Model
metadata:
name: deploy-model
spec:
url : "/models/deploy_model/saved_model.pb"
format: "pb"
EOF
Start The Incremental Learning Job
incremental learning supports hot model updates and cold model updates. Job support cold model updates default. If you want to use hot model updates, please to add the following fields:
deploySpec:
model:
hotUpdateEnabled: true
pollPeriodSeconds: 60 # default value is 60
create the job:
IMAGE=kubeedge/sedna-example-incremental-learning-helmet-detection:v0.4.0
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: sedna.io/v1alpha1
kind: IncrementalLearningJob
metadata:
name: helmet-detection-demo
spec:
initialModel:
name: "initial-model"
dataset:
name: "incremental-dataset"
trainProb: 0.8
trainSpec:
template:
spec:
nodeName: $WORKER_NODE
containers:
- image: $IMAGE
name: train-worker
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args: ["train.py"]
env:
- name: "batch_size"
value: "32"
- name: "epochs"
value: "1"
- name: "input_shape"
value: "352,640"
- name: "class_names"
value: "person,helmet,helmet-on,helmet-off"
- name: "nms_threshold"
value: "0.4"
- name: "obj_threshold"
value: "0.3"
trigger:
checkPeriodSeconds: 60
timer:
start: 02:00
end: 20:00
condition:
operator: ">"
threshold: 500
metric: num_of_samples
evalSpec:
template:
spec:
nodeName: $WORKER_NODE
containers:
- image: $IMAGE
name: eval-worker
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args: ["eval.py"]
env:
- name: "input_shape"
value: "352,640"
- name: "class_names"
value: "person,helmet,helmet-on,helmet-off"
deploySpec:
model:
name: "deploy-model"
hotUpdateEnabled: true
pollPeriodSeconds: 60
trigger:
condition:
operator: ">"
threshold: 0.1
metric: precision_delta
hardExampleMining:
name: "IBT"
parameters:
- key: "threshold_img"
value: "0.9"
- key: "threshold_box"
value: "0.9"
template:
spec:
nodeName: $WORKER_NODE
containers:
- image: $IMAGE
name: infer-worker
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args: ["inference.py"]
env:
- name: "input_shape"
value: "352,640"
- name: "video_url"
value: "file://video/video.mp4"
- name: "HE_SAVED_URL"
value: "/he_saved_url"
volumeMounts:
- name: localvideo
mountPath: /video/
- name: hedir
mountPath: /he_saved_url
resources: # user defined resources
limits:
memory: 2Gi
volumes: # user defined volumes
- name: localvideo
hostPath:
path: /incremental_learning/video/
type: DirectoryOrCreate
- name: hedir
hostPath:
path: /incremental_learning/he/
type: DirectoryOrCreate
outputDir: "/output"
EOF
The
Datasetdescribes data with labels andHE_SAVED_URLindicates the address of the deploy container for uploading hard examples. Users will mark label for the hard examples in the address.Ensure that the path of outputDir in the YAML file exists on your node. This path will be directly mounted to the container.
Check Incremental Learning Job¶
Query the service status:
kubectl get incrementallearningjob helmet-detection-demo
In the IncrementalLearningJob resource helmet-detection-demo, the following trigger is configured:
trigger:
checkPeriodSeconds: 60
timer:
start: 02:00
end: 20:00
condition:
operator: ">"
threshold: 500
metric: num_of_samples
Hard Example Labeling¶
In a real word, we need to label the hard examples in HE_SAVED_URL with annotation tools and then put the examples to Dataset‘s url.
You can use Open-Source annotation tools to label hard examples, such as MAKE SENSE, which has following main advantages:
Open source and free to use under GPLv3 license
Support outputfile formats like YOLO, VOC XML, VGG JSON, CSV
No advanced installation required, just open up your browser
Use AI to make your work more productive
Offline running as a container, ensuring data security
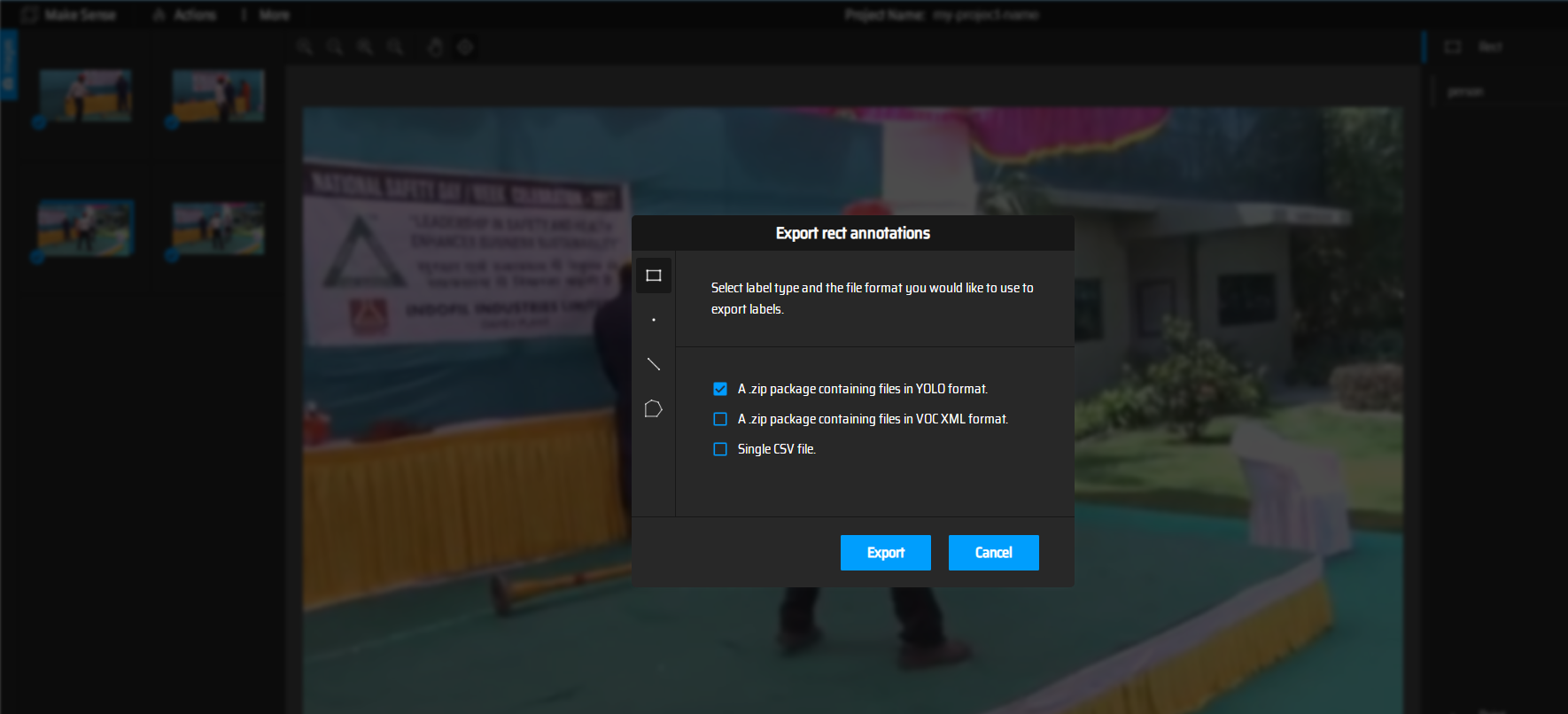
the details labeling are not described here, main steps in this demo are as follows:
import unlabeled hard example to anonotation tools

label and export annotations
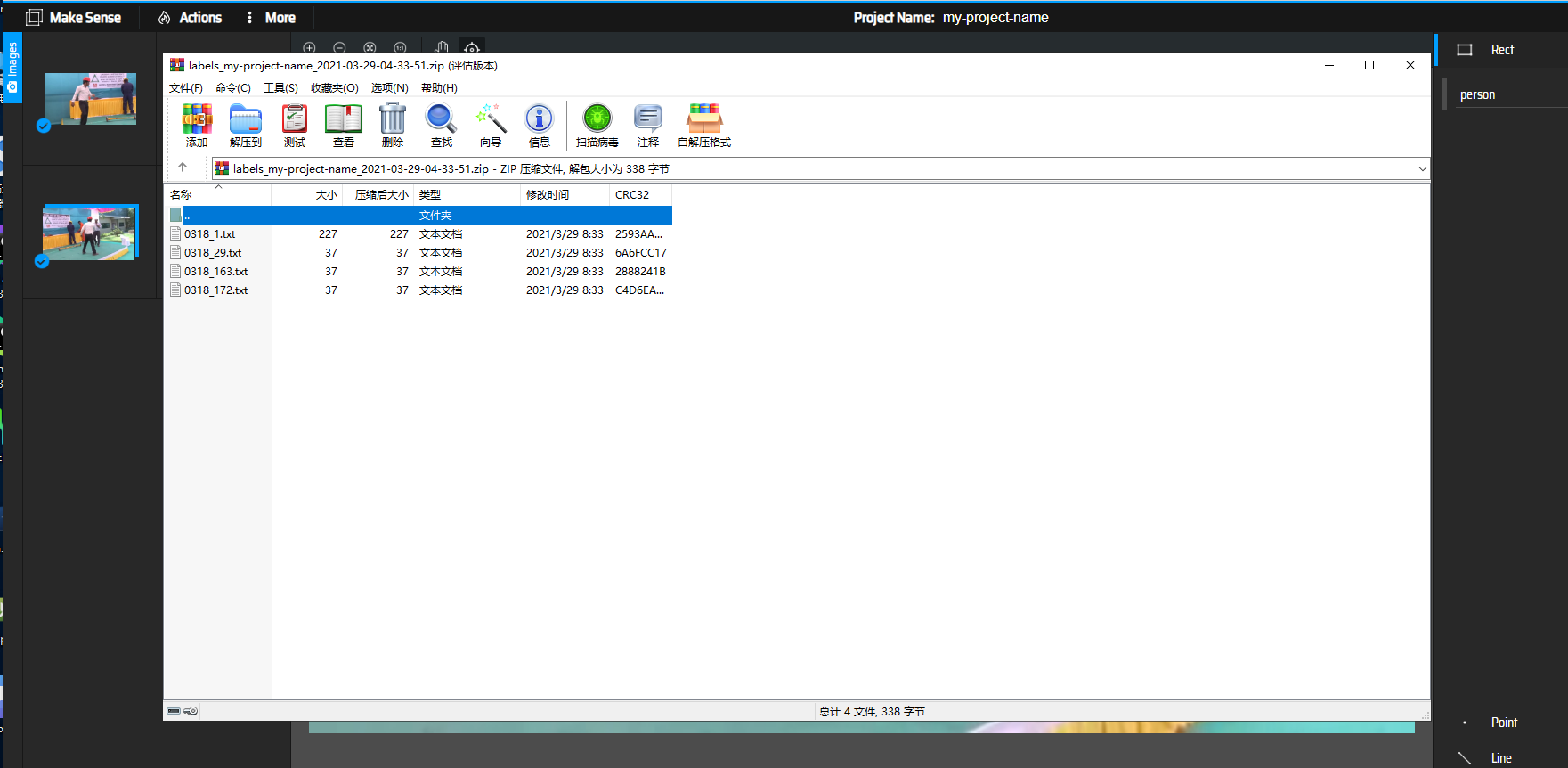
you will get YOLO format annotations, so you need convert them to the type which can be used by your own training code. in this example, the following scripts are provided for reference:
import os
annotation_dir_path = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/labeled_data"
save_path = "C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/labeled_data/save_label.txt"
def convert_single_line(line):
line_list = []
line = line.split(" ")
for i in range(1, len(line)):
line[i] = float(line[i])
line[i] = line[i] * 1000
line_list.append(str(int(line[i])))
line_list.append(line[0])
return ",".join(line_list)
if __name__ == '__main__':
results = []
g = os.walk(annotation_dir_path)
for path, dir_list, file_list in g:
for file_name in file_list:
file_path = os.path.join(path, file_name)
file_name = file_name.split("txt")
file_name = file_name[0] + 'jpg'
single_label_string = file_name
f = open(file_path)
lines = f.readlines()
for line in lines:
line = line.strip('\n')
single_label_string = single_label_string + " " + convert_single_line(line)
results.append(single_label_string)
save_file = open(save_path, "w")
for result in results:
save_file.write(result + "\n")
save_file.close()
How to use:
annotation_dir_path: location for labeled annotations from MAKESENSE
save_path: location for label txt which converted from annotations
run above script, you can get a txt which includes all label information
put the text with examples in the same dir
you will get labeled examples which meet training requirements
put these examples and annotations above to
Dataset‘s url
Without annotation tools, we can simulate the condition of num_of_samples in the following ways:
Download dataset to $WORKER_NODE.
cd /data/helmet_detection
wget https://kubeedge.obs.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com/examples/helmet-detection/dataset.tar.gz
tar -zxvf dataset.tar.gz
The LocalController component will check the number of the sample, realize trigger conditions are met and notice the GlobalManager Component to start train worker.
When the train worker finish, we can view the updated model in the /output directory in $WORKER_NODE node.
Then the eval worker will start to evaluate the model that train worker generated.
If the eval result satisfy the deploySpec‘s trigger
trigger:
condition:
operator: ">"
threshold: 0.1
metric: precision_delta
the deploy worker will load the new model and provide service.
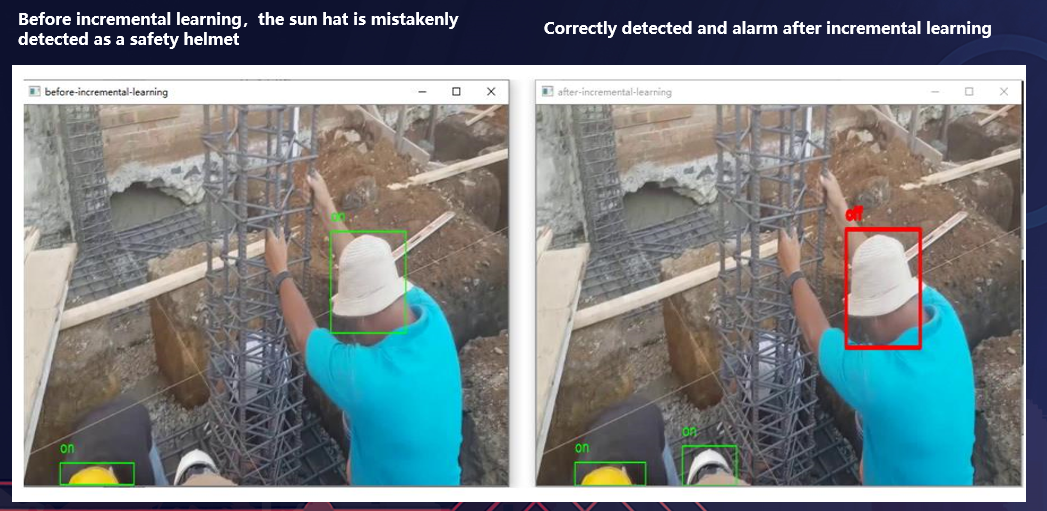
Effect Display¶
In this example, false and failed detections occur at stage of inference before incremental learning, after incremental learning, all targets are correctly detected.